Radiation exposure in hospitals poses significant risks to your health. As a healthcare professional, you may encounter radiation daily through tools like the x-ray film viewer or the x-ray indicator light. Without proper personal radiation protection in hospitals, long-term exposure can lead to severe health issues. Using dosimeters helps you monitor exposure levels, while tools like the X-ray Cassette ensure safer practices. Prioritizing safety measures safeguards your well-being and enhances workplace safety.
Key Takeaways
- Spend less time near radiation to stay safer. Plan work well to avoid extra exposure.
- Stay far from radiation machines. Use tools like long handles to work without being close.
- Wear safety gear like lead aprons and neck shields to stop harmful radiation.
Risks of Radiation Exposure in Hospitals
Health effects of radiation on healthcare professionals
Radiation exposure can harm your body in many ways. Prolonged exposure increases your risk of developing cancer, cataracts, and skin damage. High doses of radiation may also harm your bone marrow, leading to blood disorders. Even low levels of exposure over time can cause long-term health issues. As a healthcare professional, you must prioritize personal radiation protection in hospitals to reduce these risks. Protecting yourself ensures your ability to continue providing care to others.
Common sources of radiation in medical environments
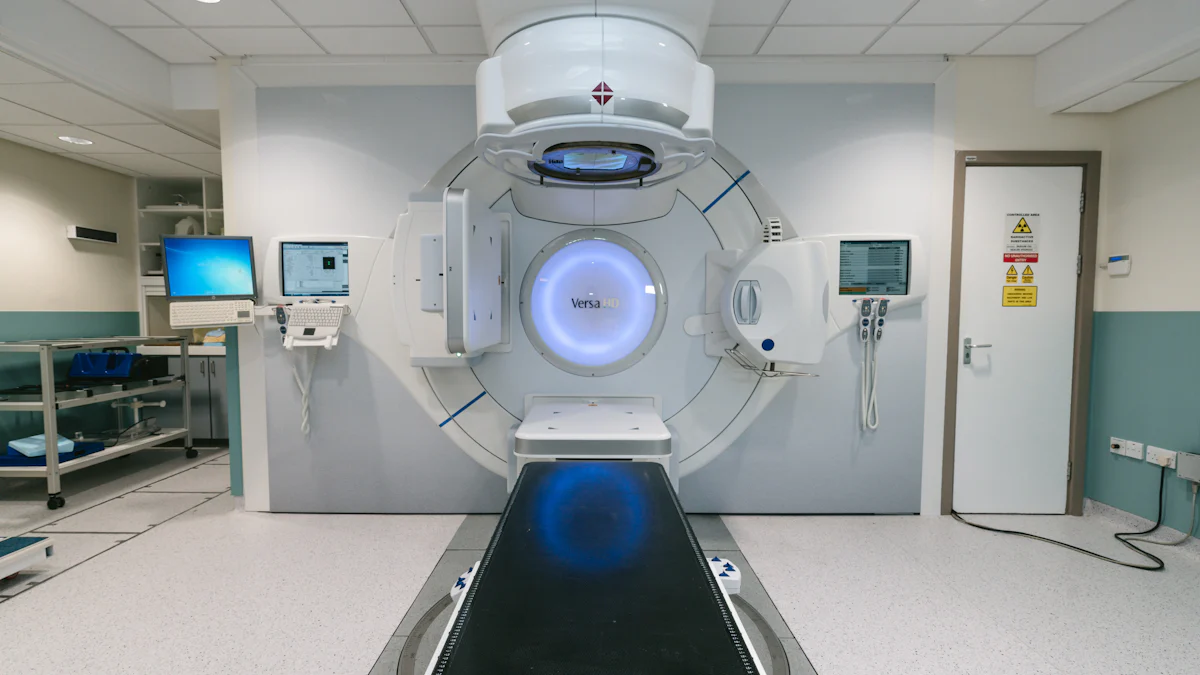
You encounter radiation in many areas of a hospital. X-ray machines, CT scanners, and fluoroscopy equipment are some of the most common sources. Nuclear medicine procedures and radiation therapy also emit radiation. Even portable imaging devices used in emergency rooms or operating theaters can expose you to radiation. Understanding where radiation comes from helps you take the right precautions. Using tools like shielding barriers and dosimeters can minimize your exposure.
Identifying vulnerable groups in healthcare settings
Certain groups in hospitals face higher risks from radiation. Radiologists, radiologic technologists, and interventional cardiologists often work near radiation-emitting devices. Nurses and surgical staff assisting in imaging procedures also face exposure. Pregnant healthcare workers require extra precautions to protect themselves and their unborn children. By recognizing these vulnerable groups, you can advocate for better personal radiation protection in hospitals and create a safer work environment for everyone.
Principles of Personal Radiation Protection in Hospitals
Time: Reducing exposure duration
Limiting the time you spend near radiation sources is one of the simplest ways to protect yourself. The less time you are exposed, the lower your risk of harm. When working with radiation-emitting equipment, plan your tasks efficiently. Organize your workflow to minimize unnecessary exposure. For example, during imaging procedures, step away from the equipment as soon as your role is complete. Always remain mindful of how long you are exposed to radiation. This practice forms a critical part of personal radiation protection in hospitals.
Distance: Maintaining safe distances
Increasing your distance from radiation sources significantly reduces your exposure. Radiation intensity decreases as you move farther away. Whenever possible, position yourself at the maximum safe distance from the source. Use tools like extension handles or remote controls to operate equipment without standing too close. In operating rooms or imaging suites, stay behind designated safety lines. By maintaining a safe distance, you can protect yourself while still performing your duties effectively.
Shielding: Using protective barriers effectively
Shielding provides a physical barrier between you and radiation. Lead aprons, walls, and mobile shields are common tools used in hospitals. Always ensure that shielding equipment is in good condition and positioned correctly. For instance, wear lead aprons during procedures involving x-rays or fluoroscopy. Use mobile shields to protect yourself when assisting with imaging. Proper shielding is essential for personal radiation protection in hospitals, as it blocks harmful rays and reduces your exposure.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Lead aprons and skirts: Features and proper use
Lead aprons and skirts are essential tools for reducing radiation exposure. These garments contain lead, which blocks harmful rays from reaching your body. You should wear them during procedures involving x-rays or fluoroscopy. Choose aprons with the right thickness for the level of radiation you face. Most aprons range from 0.25 mm to 0.5 mm lead equivalence. Thicker aprons provide better protection but may feel heavier.
Proper use is just as important as wearing the apron. Ensure it covers your torso completely, especially your chest and abdomen. Check for any cracks or damage before each use. Damaged aprons may not provide full protection. After use, hang them on designated racks to prevent creasing, which can weaken the lead lining. By using lead aprons and skirts correctly, you can enhance your personal radiation protection in hospitals.
Thyroid shields and gloves: Importance in protection
Your thyroid gland is highly sensitive to radiation. Thyroid shields protect this vital area by covering your neck. Always wear a thyroid shield during imaging procedures. Ensure it fits snugly without gaps. Loose shields may leave parts of your neck exposed.
Radiation can also harm your hands, especially if you work near x-ray beams. Lead-lined gloves provide a barrier against exposure. Use them when positioning patients or handling equipment during procedures. Inspect gloves regularly for tears or wear. Even small defects can compromise their effectiveness. Protecting your thyroid and hands reduces your overall radiation risk.
Protective eyewear: Safeguarding sensitive areas
Your eyes are vulnerable to radiation, which can cause cataracts over time. Protective eyewear shields your eyes from scattered radiation. These glasses often contain leaded lenses to block harmful rays. Wear them during procedures involving fluoroscopy or CT scans.
Choose eyewear that fits comfortably and provides full coverage. Some models include side shields for added protection. Clean the lenses regularly to maintain clear vision. Store them in a protective case when not in use. By safeguarding your eyes, you can prevent long-term damage and maintain your vision.
Best Practices for Radiation Safety

Regular training and education for healthcare staff
You need to stay informed about the latest radiation safety practices. Hospitals should provide regular training sessions to educate staff on minimizing exposure risks. These sessions can cover topics like proper equipment handling, the use of shielding tools, and emergency protocols. Training ensures you understand how to protect yourself and others effectively. Participating in refresher courses helps you stay updated on advancements in radiation safety. Knowledge empowers you to make safer decisions in your daily work.
Monitoring exposure with dosimeters
Using dosimeters is essential for tracking your radiation exposure. These devices measure the amount of radiation you absorb over time. Wear your dosimeter consistently during procedures involving radiation. Check the readings regularly to ensure your exposure stays within safe limits. If the readings show higher levels, take immediate steps to reduce your exposure. Hospitals often provide personal dosimeters for staff working in high-risk areas. Monitoring your exposure helps you maintain long-term health and safety.
Tip: Always store your dosimeter in a radiation-free area when not in use. This ensures accurate readings.
Adhering to hospital safety protocols
Following established safety protocols is critical for personal radiation protection in hospitals. These guidelines outline the correct use of protective equipment, safe distances, and proper procedures during imaging or therapy sessions. Familiarize yourself with your hospital’s specific protocols. Adhering to these rules minimizes your risk of accidental exposure. Encourage your colleagues to follow the protocols as well. A team effort creates a safer environment for everyone.
Note: Report any safety concerns or protocol violations to your supervisor immediately.
Building a Radiation Safety Culture
Leadership’s role in fostering compliance
Leadership plays a critical role in creating a culture of safety. As a healthcare leader, you set the tone for radiation safety practices. When you prioritize safety, your team follows suit. Ensure that policies for personal radiation protection in hospitals are clear and accessible. Lead by example by consistently using protective equipment and adhering to safety protocols. Provide resources and support to help your staff stay compliant. Your commitment encourages others to take radiation safety seriously.
Encouraging open communication about safety
Open communication is essential for improving safety. Encourage your team to share concerns about radiation exposure without fear of judgment. Create an environment where everyone feels comfortable discussing safety practices. Regularly hold meetings to address challenges and brainstorm solutions. When you listen to your team, you gain valuable insights into potential risks. This collaborative approach strengthens your overall safety culture. By fostering open dialogue, you empower your team to take ownership of their safety.
Continuous improvement through audits and feedback
Regular audits help you identify gaps in safety practices. Conduct routine checks to ensure compliance with radiation safety protocols. Use the findings to make necessary improvements. Feedback from staff is equally important. Ask your team for suggestions on enhancing safety measures. Implementing their ideas shows that you value their input. Track progress over time to measure the effectiveness of changes. Continuous improvement ensures that your safety culture evolves to meet new challenges.
Personal radiation protection in hospitals is essential for your health and safety. Following safety practices and using PPE reduces your exposure to harmful radiation. Make radiation safety a priority for yourself and your team. By staying vigilant and proactive, you create a safer environment for everyone in your workplace.
FAQ
What is the purpose of a dosimeter?
A dosimeter measures your radiation exposure. It helps you track how much radiation you absorb over time, ensuring your levels stay within safe limits.
How often should you inspect protective equipment?
Inspect your protective equipment before every use. Look for cracks, tears, or damage that could compromise its effectiveness. Regular checks keep you safe.
Can pregnant healthcare workers safely work near radiation?
Yes, with precautions. Use shielding, maintain distance, and limit exposure time. Always consult your hospital’s safety guidelines for additional measures to protect yourself and your baby.
Tip: Speak with your supervisor about adjusting duties if needed during pregnancy.
Post time: Feb-07-2025